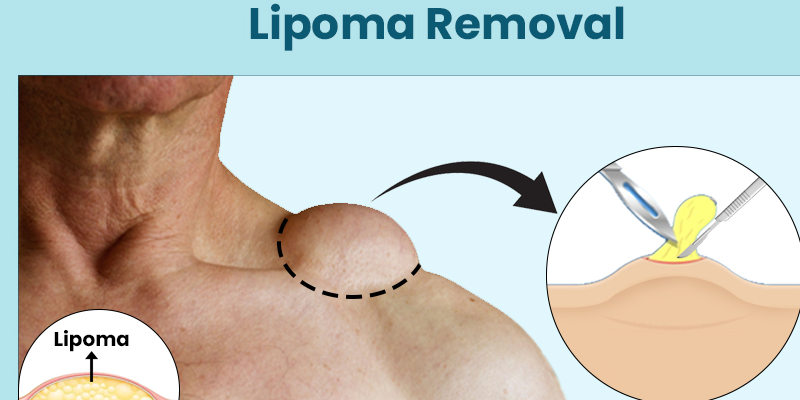
Lipoma Removal Surgeries
A lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) fatty lump that develops under the skin. It is usually soft, painless, and slow-growing. Lipomas can occur anywhere in the body where fat cells are present, but they are most commonly found on the neck, shoulders, arms, back, abdomen, and thighs. While lipomas are generally harmless, some people choose to have them removed for cosmetic reasons, discomfort, or if the lump grows large or causes functional problems. Lipoma removal surgery is a safe and effective procedure performed to excise the lump and prevent recurrence.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of lipomas is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to their development:
– Genetic predisposition (family history of lipomas)
– Middle-aged adults (most common between 40–60 years)
– Certain inherited conditions such as familial multiple lipomatosis
– Minor injuries or trauma to soft tissue
– Obesity or metabolic disorders (though lipomas can occur in people of any body type)
Symptoms of a Lipoma
While most lipomas are painless, some may cause discomfort if they press on nerves or grow near joints. Common signs include:
– A soft, doughy lump under the skin
– Slow, steady growth over months or years
– Movement of the lump under gentle pressure
– Occasional tenderness if located near nerves or muscles
Diagnosis
Diagnosis usually begins with a physical examination. In most cases, the texture, mobility, and appearance of the lump are sufficient for diagnosis. If the lump is unusually hard, painful, or fixed in place, the doctor may recommend imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan to rule out other conditions. A biopsy may be performed if there is any suspicion of malignancy.
Treatment Options
The only definitive treatment for a lipoma is surgical removal. There are several techniques:
– Excision Surgery: The most common method where the surgeon makes a small incision, removes the lipoma, and closes the wound with stitches.
– Minimal Incision Extraction: A smaller cut is made to remove the lipoma with less scarring.
– Liposuction-Assisted Removal: A thin tube is inserted to suction out the fatty tissue (best for softer, less fibrous lipomas).
– Laser-Assisted Removal: In selected cases, lasers may be used for minimal bleeding and quicker healing.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from lipoma removal surgery is generally quick. Most patients can resume normal activities within a day or two, though strenuous exercise should be avoided until the incision heals. Proper wound care, as advised by the surgeon, helps prevent infection and minimize scarring. Stitches are usually removed within 7–14 days, depending on the location and size of the incision.
Final Thoughts
Lipomas are common and usually harmless, but they can sometimes cause discomfort, functional limitations, or cosmetic concerns. Surgical removal is a simple, safe, and effective way to eliminate the lump permanently. If you notice a new lump or a change in an existing one, consult a qualified surgeon to confirm the diagnosis and discuss the best removal option for you.

