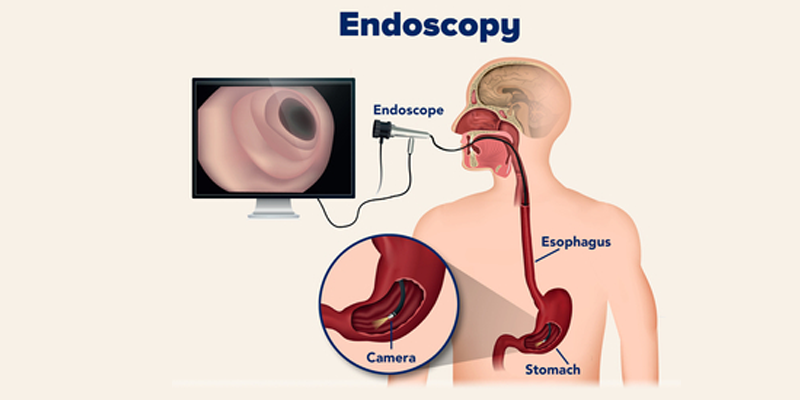
Endoscopic Procedures (Upper GI Endoscopy & Colonoscopy)
Endoscopic procedures are advanced, minimally invasive techniques used to diagnose and treat conditions within the digestive tract. Two of the most common types are Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Endoscopy and Colonoscopy. Both procedures use a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light (endoscope) to capture detailed images of the digestive tract, helping doctors detect diseases early and perform treatments without major surgery.
Upper GI Endoscopy
Also known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), an Upper GI Endoscopy examines the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). It is used to investigate symptoms such as persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, chronic nausea, or unexplained stomach pain. The procedure can also detect ulcers, inflammation, tumors, and early signs of cancer.
Colonoscopy
A Colonoscopy examines the large intestine (colon) and rectum. It is widely used to screen for colorectal cancer, investigate causes of bleeding, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain, and remove precancerous growths (polyps). Early detection through colonoscopy is one of the most effective ways to prevent colorectal cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors Requiring Endoscopy
Endoscopic procedures are recommended for various digestive issues. Some common causes and risk factors include:
– Persistent or severe digestive symptoms
– Family history of gastrointestinal cancer
– Blood in stool or vomit
– Unexplained weight loss
– Chronic acid reflux or indigestion
– Screening for colorectal cancer (especially over age 45)
Diagnosis Process
Before an Upper GI Endoscopy, patients are asked to fast for several hours to ensure a clear view. For Colonoscopy, bowel preparation with a special cleansing solution is required to empty the intestines. Sedation or anesthesia is usually given for comfort. The doctor then inserts the endoscope through the mouth (for Upper GI Endoscopy) or the anus (for Colonoscopy) to examine the digestive tract.
Treatment Capabilities
In addition to diagnosis, these procedures can be used for treatment:
– Removing polyps or abnormal growths
– Stopping gastrointestinal bleeding
– Dilating narrowed areas of the digestive tract
– Taking tissue samples (biopsy) for further testing
Benefits of Endoscopic Procedures
– Minimally invasive with quick recovery
– Early detection of serious conditions like cancer
– Ability to treat during diagnosis
– High accuracy and detailed imaging
– Outpatient procedure with same-day discharge
Recovery and Aftercare
Most patients can go home the same day. Mild throat discomfort, bloating, or gas may occur temporarily. Strenuous activity should be avoided for 24 hours, and patients should follow dietary instructions from their doctor. If any unusual symptoms like severe pain, fever, or bleeding occur, immediate medical attention is advised.
Final Thoughts
Upper GI Endoscopy and Colonoscopy are safe, effective, and essential tools in diagnosing and preventing gastrointestinal diseases. They combine precision imaging with therapeutic capabilities, allowing early intervention and better patient outcomes. If you have persistent digestive symptoms or are due for a screening, consult a qualified gastroenterologist to determine the right endoscopic procedure for you.

