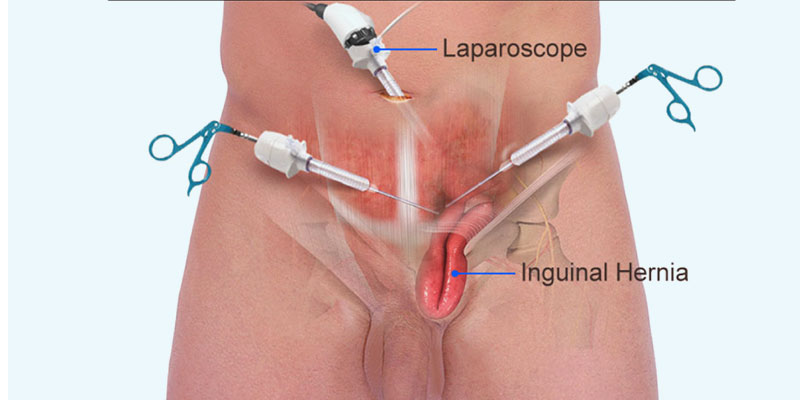
Hernia Repair (Open and Laparoscopic)
Hernia repair surgery is a procedure to correct a hernia, which occurs when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Hernias are most common in the abdomen or groin area and can cause pain, discomfort, or other complications if left untreated. Hernia repair can be performed using two main approaches—open surgery or laparoscopic (minimally invasive) surgery—both designed to restore strength to the weakened area and prevent recurrence.
Causes and Risk Factors
Hernias can develop due to a combination of muscle weakness and strain. Common causes and risk factors include:
– Heavy lifting without proper technique
– Chronic coughing or sneezing
– Pregnancy and childbirth
– Obesity
– Straining during bowel movements or urination
– Previous abdominal surgery
– Aging and natural wear of muscle tissues
Symptoms That May Require Surgery
While some small hernias may not cause symptoms, surgery is often recommended when symptoms worsen or complications develop. Common signs include:
– A visible bulge in the abdomen or groin
– Pain or discomfort, especially when bending, coughing, or lifting
– Swelling or pressure in the affected area
– A heavy or dragging sensation in the abdomen
– Nausea or vomiting (in case of strangulated hernia)
– Sudden severe pain indicating a medical emergency
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination where the doctor checks for a bulge that becomes more noticeable when standing or straining. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis, assess the size of the hernia, and determine the best surgical approach.
Treatment Options
Hernia repair is the definitive treatment and can be performed in two main ways:
– Open Hernia Repair: The surgeon makes an incision over the hernia site, pushes the protruding tissue back into place, and strengthens the weakened area with stitches or mesh. This method is highly effective and suitable for larger or complicated hernias.
– Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: A minimally invasive approach using small incisions and a camera to guide the repair. Mesh is usually placed to reinforce the muscle. This method offers faster recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery time depends on the surgical method used. Most laparoscopic patients return to normal activities within 1–2 weeks, while open surgery may require 3–4 weeks of healing. Post-surgery care includes avoiding heavy lifting, following a healthy diet to prevent constipation, and attending follow-up appointments. Pain and swelling are usually temporary and manageable with prescribed medications.
Final Thoughts
Hernia repair, whether open or laparoscopic, is a safe and effective procedure to relieve discomfort and prevent serious complications. Early diagnosis and timely surgery ensure the best outcomes. If you notice a bulge or experience persistent abdominal or groin pain, consult a qualified surgeon to discuss your treatment options and choose the method best suited to your needs.

