Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, is a medical procedure performed to help individuals with severe obesity achieve significant and sustainable weight reduction. It is recommended when diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes have not been effective, or when obesity is causing serious health problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, or sleep apnea. Bariatric surgery works by altering the digestive system, either by reducing the stomach size, restricting food intake, or changing how the body absorbs nutrients. With modern minimally invasive techniques, bariatric surgery has become safer, more effective, and offers long-term benefits for overall health and quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors
Obesity can develop due to multiple factors, and while genetics play a role, lifestyle and environmental influences are often the main contributors. Some of the common causes and risk factors that may lead to the need for bariatric surgery include:
– Excessive calorie intake and unhealthy diet
– Lack of physical activity and sedentary lifestyle
– Genetic predisposition to obesity
– Hormonal or metabolic disorders
– Emotional eating or stress-related eating habits
– Family history of obesity and related conditions
– Long-term use of certain medications such as steroids or antidepressants
Symptoms That May Require Surgery
Bariatric surgery is not just about weight loss but about addressing health complications linked to obesity. A patient may be considered for surgery if the following symptoms or conditions are present:
– Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher
– BMI of 35 or higher with serious health conditions like diabetes or hypertension
– Severe sleep apnea or breathing difficulties
– Persistent joint pain due to excess weight
– Difficulty performing everyday activities
– Unsuccessful attempts at losing weight through diet and exercise
Diagnosis
Before recommending bariatric surgery, doctors conduct a thorough evaluation to determine if the patient is a suitable candidate. This typically includes a complete medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Imaging studies and cardiac assessments may also be required to rule out risks. Patients are usually advised to undergo psychological evaluation, as mental health plays an important role in long-term weight management. A multidisciplinary team, including surgeons, dietitians, and endocrinologists, works together to ensure the patient is well-prepared for surgery.
Types of Bariatric Surgery
There are different surgical options available, and the choice depends on the patient’s health condition, weight loss goals, and surgeon’s recommendation. The most common types of bariatric surgery include:
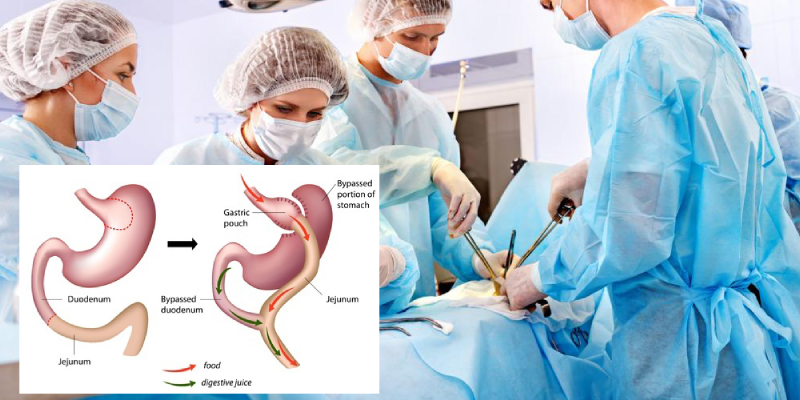
– Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y): One of the most widely performed procedures where the stomach is divided into a small pouch and connected directly to the small intestine, bypassing a portion of the digestive tract. This reduces calorie absorption and limits food intake.
– Sleeve Gastrectomy: In this procedure, a large portion of the stomach is removed, leaving a banana-shaped sleeve. It significantly reduces the stomach’s capacity, helping patients feel full faster while maintaining normal digestion.
– Adjustable Gastric Banding: A silicone band is placed around the upper portion of the stomach to create a smaller pouch. The band can be adjusted to control food intake. Although less common today, it remains an option for select patients.
– Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS): A more complex surgery that combines stomach reduction with significant intestinal bypass, leading to reduced calorie and nutrient absorption. It is typically reserved for patients with extreme obesity.
Recovery and Lifestyle Changes
Recovery after bariatric surgery depends on the type of procedure, but most minimally invasive surgeries allow patients to return home within a few days. A liquid and soft food diet is followed initially, gradually progressing to normal meals under medical guidance. Patients must adopt lifelong dietary changes, including smaller portion sizes, high-protein meals, and regular vitamin supplementation to prevent nutritional deficiencies. Regular physical activity, follow-up checkups, and counseling are essential for long-term success.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery offers numerous health benefits beyond weight reduction. These include:
– Long-term weight loss and improved quality of life
– Better control of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cholesterol levels
– Reduction in sleep apnea and breathing problems
– Decreased risk of heart disease and stroke
– Relief from joint pain and improved mobility
– Boosted self-confidence and psychological well-being

