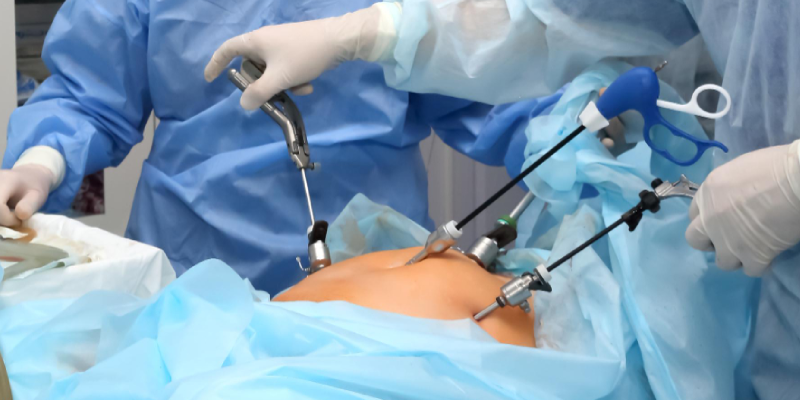
Laparoscopic Surgeries
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique that allows doctors to perform operations through small incisions using a laparoscope—a thin tube with a camera and light attached. Unlike traditional open surgery, laparoscopic procedures involve minimal cuts, less pain, quicker recovery, and reduced hospital stay. The laparoscope projects real-time images onto a monitor, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy and precision. Today, laparoscopic surgery is widely used for abdominal and pelvic conditions, offering safer and more effective alternatives to conventional methods.
Causes and Conditions Treated
Laparoscopic surgery is performed for a variety of medical conditions, particularly those affecting the abdominal and pelvic regions. Common conditions and causes that may require laparoscopic intervention include:
– Gallstones and gallbladder diseases
– Hernias (inguinal, umbilical, or incisional)
– Appendicitis
– Ovarian cysts and gynecological disorders
– Endometriosis
– Gastrointestinal problems such as ulcers, bowel obstruction, or reflux
– Liver, pancreas, or spleen-related disorders
– Bariatric (weight loss) surgery
– Diagnostic purposes when non-invasive tests are inconclusive
Symptoms That May Require Surgery
Depending on the underlying condition, laparoscopic surgery may be recommended if the following symptoms are experienced:
– Severe and persistent abdominal pain
– Unexplained swelling or bloating
– Digestive difficulties and chronic indigestion
– Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
– Hernia-related swelling or discomfort
– Gynecological symptoms such as painful periods or pelvic pain
– Abnormal imaging results requiring further evaluation
Diagnosis
Before recommending laparoscopic surgery, doctors conduct a comprehensive evaluation. This includes medical history, physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, and sometimes endoscopy. If necessary, a diagnostic laparoscopy may be performed to visually examine the internal organs and confirm the diagnosis before proceeding with treatment.
Types of Laparoscopic Surgeries
Laparoscopic techniques can be applied to several surgical procedures across specialties. Common types include:
– Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder, most often due to gallstones causing pain or infection.
– Laparoscopic Appendectomy: Surgical removal of the appendix in cases of acute appendicitis.
– Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: Repair of inguinal, umbilical, or incisional hernias using mesh reinforcement.
– Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy: Removal of ovarian cysts while preserving reproductive organs.
– Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus for conditions such as fibroids, endometriosis, or abnormal bleeding.
– Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery: Weight loss procedures like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.
– Laparoscopic Colectomy: Removal of part of the colon for cancer, diverticulitis, or inflammatory bowel disease.
Recovery and Post-Surgery Care
One of the biggest advantages of laparoscopic surgery is the faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery. Most patients are able to go home within 24–48 hours, depending on the procedure. Initial discomfort, mild swelling, or shoulder pain due to carbon dioxide used during surgery may be experienced but typically resolve within a few days. Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting for a few weeks, follow a healthy diet, and attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing. Early mobilization and breathing exercises also help speed up recovery.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgeries
Laparoscopic techniques have transformed modern surgical care by providing numerous benefits, such as:
– Smaller incisions with minimal scarring
– Reduced pain and blood loss during surgery
– Shorter hospital stays and faster return to daily activities
– Lower risk of infection compared to open surgery
– Greater surgical precision with improved visualization
– Enhanced patient comfort and better cosmetic outcomes

