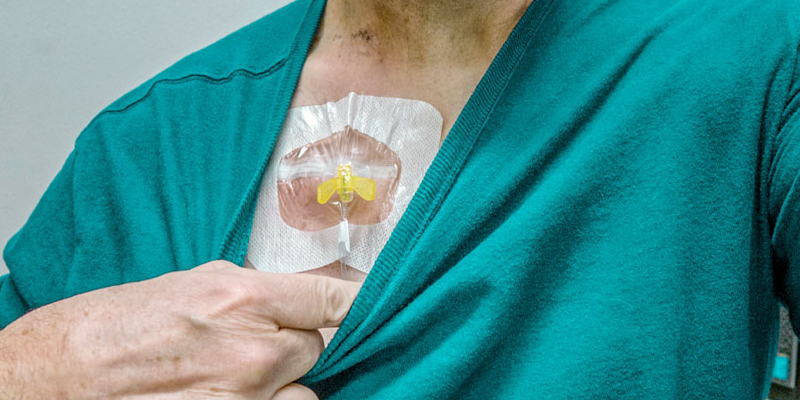
Chemoport Management
Chemoport management is an essential aspect of cancer care, helping patients receive chemotherapy safely and comfortably. A chemoport, also known as an implantable port or port-a-cath, is a small medical device placed under the skin, usually in the chest. It is connected to a vein through a catheter and provides direct access to the bloodstream. This allows for repeated chemotherapy sessions, blood draws, and medication administration without the need for frequent needle pricks in the veins.
What is a Chemoport?
A chemoport is a soft, silicone-based device surgically implanted beneath the skin. It has two main components:
– The port reservoir: A small chamber placed under the skin, where the chemotherapy needle is inserted.
– The catheter: A thin flexible tube that connects the port to a large central vein, usually in the neck or chest.
Once placed, the chemoport can remain in the body for months or even years, depending on the treatment plan.
Why is Chemoport Management Important?
Proper management of a chemoport ensures safe, effective, and complication-free cancer treatment. Key reasons include:
– Reducing the discomfort of repeated needle sticks.
– Preventing damage to peripheral veins from frequent chemotherapy sessions.
– Allowing quick and reliable access to the bloodstream.
– Minimizing risks of infection or clot formation.
– Ensuring smooth delivery of chemotherapy drugs and IV medications.
Chemoport Insertion Procedure
The insertion of a chemoport is a minor surgical procedure usually done under local anesthesia with sedation. Steps typically include:
– Cleaning and numbing the skin with local anesthesia.
– Making a small incision in the chest area.
– Inserting the port under the skin and connecting it to a vein with the catheter.
– Closing the incision with sutures and applying a dressing.
– Post-procedure X-ray may be done to confirm correct placement.
Most patients go home the same day, and the site heals within a week.
Chemoport Care and Management
Proper care of a chemoport is crucial to avoid complications. Important management guidelines include:
– Flushing the port with saline and heparin solution to prevent blockage.
– Keeping the site clean and covered during use.
– Regularly checking for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or pain.
– Ensuring the port is accessed only by trained medical professionals.
– Following the oncologist’s schedule for port maintenance when not in regular use.
Benefits of Chemoport
Patients undergoing long-term chemotherapy gain multiple benefits from a chemoport, such as:
– Less pain and discomfort compared to repeated IV insertions.
– Long-term use without frequent replacements.
– Lower risk of vein irritation or damage.
– Safer administration of chemotherapy drugs.
– Convenience for both patients and healthcare providers.
Risks and Complications
Although generally safe, chemoports may rarely cause complications. These may include:
– Infection at the insertion site.
– Blockage or clot formation inside the catheter.
– Displacement of the port or catheter.
– Mild bruising or swelling after insertion.
Most complications can be prevented with proper care and timely medical attention.
Conclusion
Chemoport management plays a vital role in the treatment journey of cancer patients. By ensuring proper care, cleaning, and maintenance, patients can safely receive chemotherapy with minimal discomfort. A well-managed chemoport not only improves the efficiency of cancer treatment but also enhances patient comfort and overall quality of life during therapy.

